What is Composting
Mechanism
Composting is a controlled, biological process of decomposing raw organic waste materials such as dead leaves and kitchen scraps. Microorganisms including bacteria, fungi, and worms break them down to compost, a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
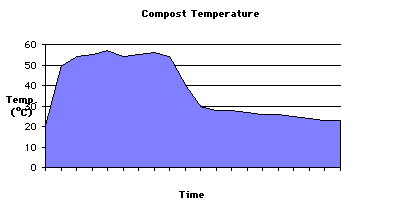
In the active phase of composting, metabolic work of microorganisms rapidly heats up the compost pile to temperatures typically in the range of 50-65°C (120-150°F), high enough to kill pathogens and toxic compounds to plants.
When the active phase subsides, the temperatures gradually decline to about 100°F and also the rate of oxygen consumption to a level where the compost pile can remain stockpiled without much turning. Under an optimal condition of oxygen, moisture, pH, and salinity levels, the compost pile can undergo months of final composting period which would be concluded by the time of complete conversion of organic materials to humic substances resistant to microbial decomposition.


Permaculture Research Institute
https://www.permaculturenews.org/2017/01/12/small-scale-composting/
Compostables
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Eggshells
-
Coffee grounds and filters
-
Tea bags
-
Nut shells
-
Shredded newspaper
-
Cardboard
-
Paper
-
Yard trimmings
-
Grass clippings
-
Houseplants
-
Hay and straw
-
Leaves
-
Sawdust
-
Wood chips
-
Cotton and Wool Rags
-
Dryer and vacuum cleaner lint
-
Hair and fur
-
Fireplace ashes
Reference
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
https://www.epa.gov/recycle/composting-home










Non-compostables
-
Black walnut tree leaves or twigs
-
Coal or charcoal ash
-
Dairy products (e.g., butter, milk, sour cream, yogurt) and eggs
-
Diseased or insect-ridden plants
-
Fats, grease, lard, or oils
-
Meat or fish bones and scraps
-
Pet wastes (e.g., dog or cat feces, soiled cat litter)
-
Yard trimmings treated with chemical pesticides





Benefits of Composting
-
Enriches soil by helping it retain moisture and suppress plant pathogens and pests
-
Reduces the need for chemical fertilizers
-
Encourages the production of beneficial bacteria and fungi that break down organic matter to create humus, a rich nutrient-filled material
-
Reduces methane emissions from landfills and lowers your carbon footprint



